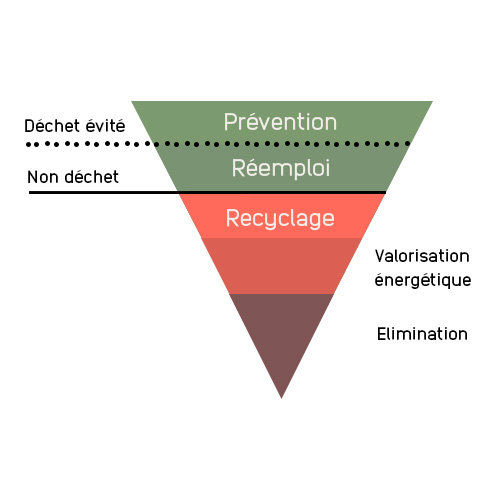
Recycling of products or materials from the building sector
How to define the recycling of building products and materials?
Recycling is a process of treating waste materials so that they can be reintroduced into the manufacturing process of new products for their original function or for other purposes.
It is an essential process for the circularity of resources to move towards the circular economy. According to ADEME, "this is a sustainable development issue, in a world where the growing consumption of natural resources raises the question of the planet's limits. But it is also a strategic economic and industrial issue for France - and more broadly for Europe - because, in a territory that depends mainly on imports for most of the materials and fossil fuels necessary for the production of its material goods, recycling is a lever for independence, preservation of value, and therefore of activity and jobs.

What are the challenges of recycling PMCB?
Already concerned by several regulatory targets, the construction sector currently recycles an average of nearly 33% of its inert waste, thanks in particular to the 30 million tons of mineral materials (PMCB) such as concrete that can be recycled into aggregate for roadways. The recycling rate for construction waste is 37%.
One of the major challenges of the sector will be to facilitate the free collection of waste and to strengthen the territorial network of collection points to encourage the deposit of waste and thus work on the elimination of illegal dumping, whose cost to local authorities is estimated at between 340 and 420 million euros, but also to increase the rate of recycling and recovery of construction waste products (PMCB).
What are the alternatives to landfill?
There are several alternatives to landfilling construction waste:
- Reuse allows us to recover materials before they are thrown away, in order to give them a second life.
- Reuse is the re-use of a product or material that has become waste.
- Recovery consists in fighting against the burying of waste by giving it value. There are three types of recovery:
- Material recovery: using the waste material for a new production process (recycling).
- Organic recovery: composting and methanization of organic waste.
- Energy recovery: using waste incineration to create heat to power heating and electricity systems.
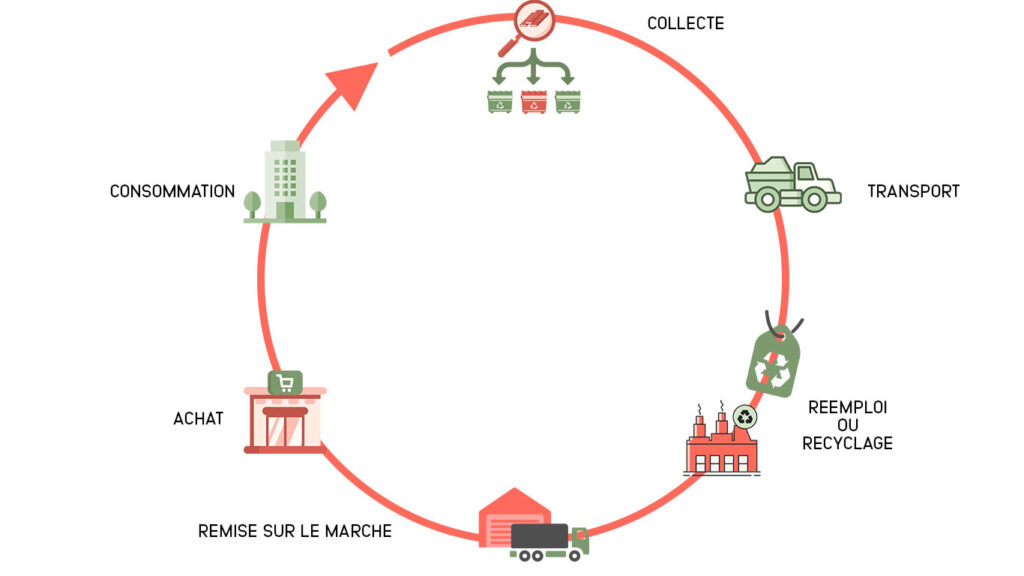
What is the PMCB waste collection cycle?
What are the different recyclable PMCB channels ?
The different PMCB streams are separated into two:
Category 1 includes building products and materials made up mainly of minerals that do not contain glass, mineral wool or gypsum (concrete and mortar, lime, limestone, granite, sandstone and lava, baked or raw earth, slate, bituminous mix, etc.).
Category 2 covers other building products and materials in the following families:
- Construction products and materials made up of a majority of metal, wood, plastic or bituminous membranes.
- Mortars, coatings, paints, varnishes, resins, preparation and implementation products, including their container.
- Joinery with glass, glass walls and related construction products.
- Building products and materials based on glass wool, rock wool or plaster.
- Construction products of plant, animal or other materials
An order of the Minister of the Environment may specify the list of products concerned.
Discover recycling by sector
How does Valobat intervene in the recycling of PMCB waste?
Valobat intervenes at the source by proposing a sorting of the PMCB directly on the building sites of deconstruction, renovation or construction.
Calls for tenders conducted by Valobat
Valobat has launched a tender procedure that will be carried out in several phases and will cover the following services
- The "Collection-Triage-Massification" market. It allows the selection of partners with the skills to collect (public waste collection centers, professional waste collection centers, distributors, etc.), separate and massify the waste flows before evacuation to a preparation center.
- The two "Woodwork" markets. They allow the specialized collection as well as the dismantling/treatment of glazed joineries.
- The four "Preparation" markets: They consist in choosing the partners who can manage the production operations of secondary materials in accordance with the specifications of the incorporation industries.



